Why You Should Enable Debug in WordPress? When something goes wrong on your WordPress website—like a plugin conflict, theme issue, or white screen of death—debugging is the first step toward finding and fixing the problem. WordPress comes with a built-in debugging system that helps developers and site owners diagnose issues quickly.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll show you exactly how to enable debug mode in WordPress, explain what each debugging tool does, and walk you through best practices to keep your site safe and error-free.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What Is Debug Mode in WordPress?
- 2 Before You Begin to Enable Debug in WordPress
- 3 How to Enable WordPress Debug Mode (Step-by-Step)
- 4 Final Example of a Secure Debug Configuration
- 5 Where to Find the Debug Log
- 6 Enable Debugging for Scripts and Styles (Advanced)
- 7 WP_DEBUG Tools for Plugin and Theme Developers
- 8 Best Practices for Debugging WordPress
- 9 How to Disable Debug Mode in WordPress
- 10 Conclusion
- 11 FAQs About Complete Guide to Enable Debug in WordPress
What Is Debug Mode in WordPress?
Debug mode is a feature in WordPress that helps you see and log PHP errors, warnings, and notices generated by your site’s themes, plugins, or core files. When enabled, it provides valuable error messages that are otherwise hidden, allowing you to identify the source of issues more efficiently.
Enable WordPress Debugging is crucial for:
- Troubleshooting plugin and theme errors
- Identifying deprecated functions
- Capturing fatal PHP errors
- Logging problems without showing them to visitors
Before You Begin to Enable Debug in WordPress
Important Note About Enable Debugging in WordPress: Never enable debug mode on a live website without hiding errors from public view. Exposing debug information can leak sensitive data like file paths, plugin versions, or server configurations—making your site more vulnerable to attacks.
We’ll show you how to safely log errors without displaying them to visitors.
How to Enable WordPress Debug Mode (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Access Your wp-config.php File
To enable wordpress debugging, you need to edit the wp-config.php file located in the root directory of your WordPress installation. You can access it via:
- cPanel File Manager – you can login to your wordpress website and enter the file manager, open public_html folder and find wp-config.php file then go to next step for enable wordpress debug. this is similar for Direct Admin Plesk and other Webhosting Panels too.
- FTP Client (like FileZilla) – also you can conntect to FTP using filezilla and open public_html folder to find the wp-config.php file
- SSH (if you have root access) you can use cd command to go too the root of the website, command is like :
cd /home/username/public_htmlthe SSH Way is for professional users who knows a lot about command line and linux commands, if you want the easiest way, i recommend to use your webhosting panel file manager.
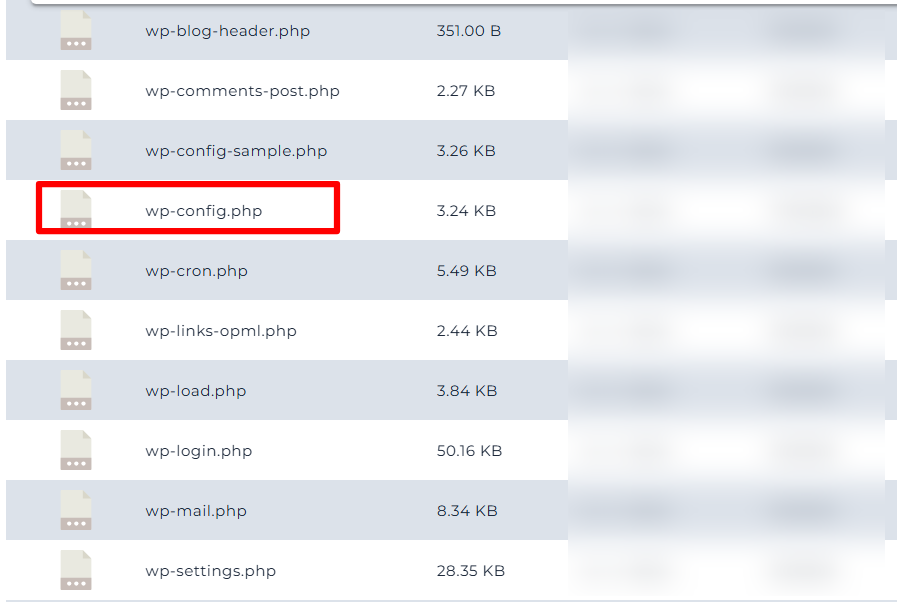
Tip: Always make a backup before editing core files. you can copy the wp-config.php file to your computer, or make a copy of it online before enabling wordpress debug.
Step 2: Add or Modify Debug Constants
Open the wp-config.php file and look for this line (near the bottom):
define(‘WP_DEBUG’, false);
To enable debugging, change it to:
define(‘WP_DEBUG’, true);
If the line doesn’t exist, you can add it just above this line:
/* That’s all, stop editing! Happy blogging. */
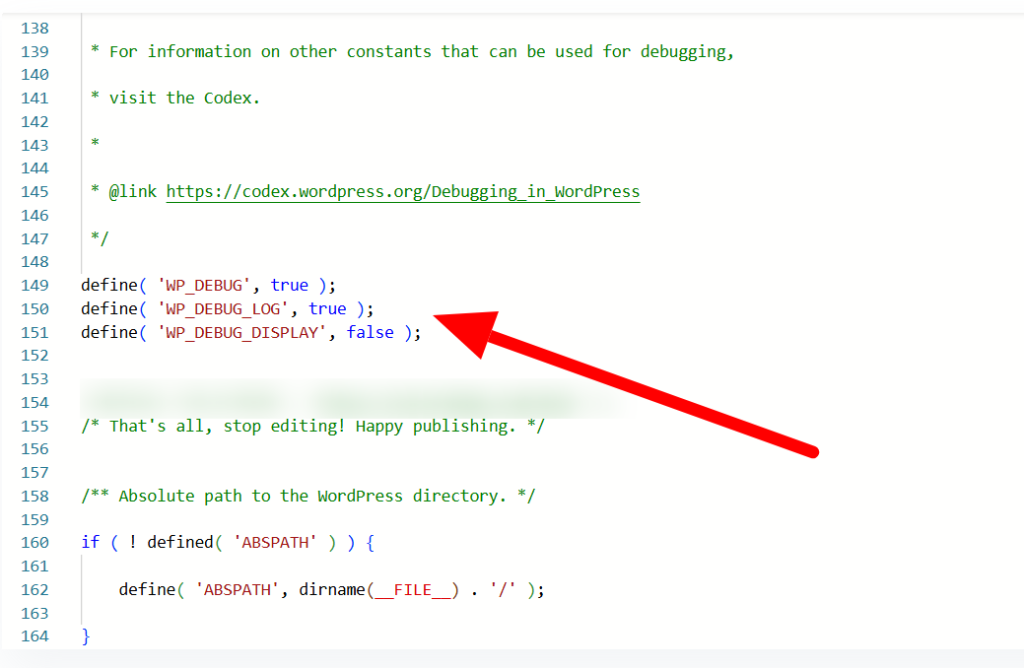
if you are trying to edit file using FileZilla, you can right-click the wp-config file and click on the Edit.
Step 3: Enable Debug Logging (Optional but Recommended for Enable WordPress Debugging)
Instead of displaying errors on the screen, it’s safer to log them to a file. Add this below the WP_DEBUG line:
define(‘WP_DEBUG_LOG’, true);
This will create a debug.log file in the /wp-content/ directory, which records all errors silently.
Step 4: Hide Errors from Displaying on Screen
To prevent errors from showing up on the frontend (especially on a live site), disable error display by adding:
define(‘WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY’, false);
@ini_set(‘display_errors’, 0);
Now, even though debugging is enabled, users won’t see sensitive information on your site.
Final Example of a Secure Debug Configuration
Here’s what your debug section should look like in wp-config.php:
define(‘WP_DEBUG’, true);
define(‘WP_DEBUG_LOG’, true);
define(‘WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY’, false);
@ini_set(‘display_errors’, 0);
Where to Find the Debug Log
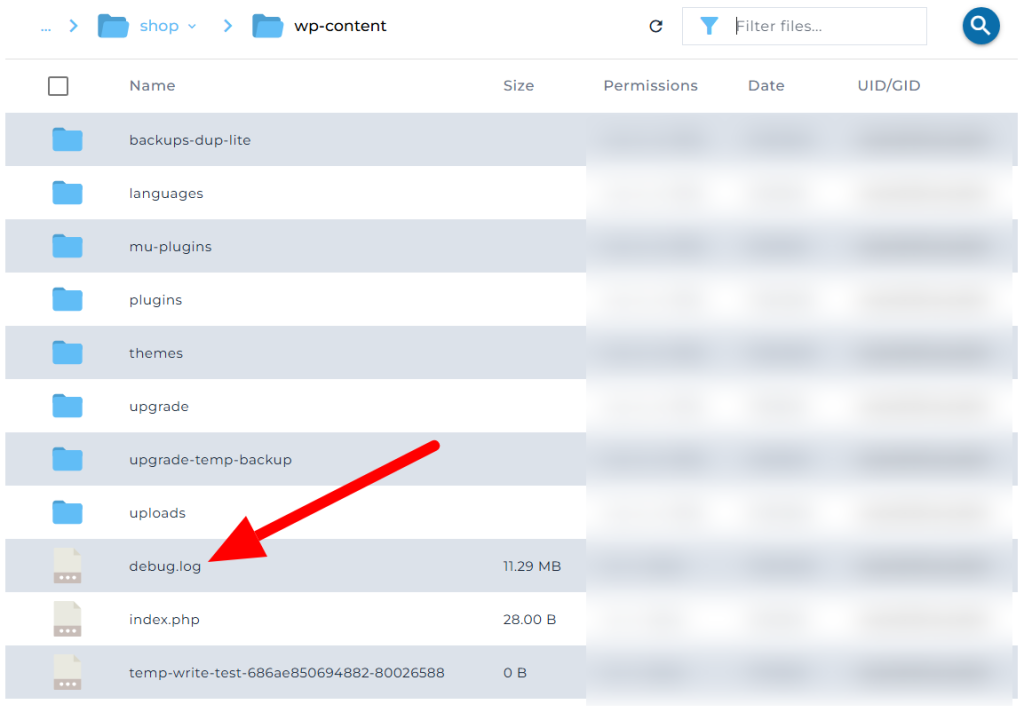
Once errors are triggered, WordPress writes them to a file called debug.log in this path:
/wp-content/debug.logYou can view the log using:
- File Manager in your hosting panel
- FTP client
- SSH (using cat wp-content/debug.log)
Important Note: if you want to leave the “wordpress debug” true for a while, this file will grow fast easily( 1-2 gigabytes or more) and fill your webhosting drive, causing “webdisk is full” error. always check this file size to prevent future problems.
Enable Debugging for Scripts and Styles (Advanced)
If you’re developing themes or plugins, you can go further by disabling the minified versions of core scripts and styles.
Add this to wp-config.php:
define('SCRIPT_DEBUG', true);This tells WordPress to use the full versions of wp-admin and frontend scripts, which makes debugging easier.
WP_DEBUG Tools for Plugin and Theme Developers
Here are a few other debug constants you can use:
1. SAVEQUERIES
Records all database queries and how long they take. Useful for performance tuning.
define('SAVEQUERIES', true);Note: Enabling this can slow down your site. Use only in development. and if you are trying to actually find out about query and performance in wordpress i recommend to use Query Monitor Plugin. it has a great UI that you can actually see the performance and queries Page By Page. it’s very useful tool to check the performance of database and a good help to wordpress debug in the database queries.
2. WP_LOCAL_DEV
This tells WordPress your environment is local, which some plugins and themes use to conditionally load code.
define('WP_LOCAL_DEV', true);you should not use this on a production site, it will break some plugins functionality. use this on you local or staging website, btw this is almost useless in the wordpress debug, but useful to localhost installed wordpress.
Best Practices for Debugging WordPress
- Use staging environments: it’s better to debug on a staging website (if your website is working fine after the error)
- Disable debug mode when done: Leaving debug mode enabled on a live site can pose security risks. also showing notices from third-party plugins will cause bad visual impact on the frontend of your website.
- Monitor logs regularly: Catch silent PHP errors before they become serious.
- Combine with browser dev tools: Use browser developer consoles for debugging JavaScript or CSS issues.
How to Disable Debug Mode in WordPress
We Have A Complete Article About “How To Disable Debug in WordPress” which you can read later. but just for a quick look on How to disable Debug in Your WordPress Website, Once you’re done troubleshooting, turn off debug mode by editing your wp-config.php again:
define(‘WP_DEBUG’, false);
define(‘WP_DEBUG_LOG’, false);
define(‘WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY’, false);
Also, delete the debug.log file to clean up your server.
Conclusion
Debugging is one of the most powerful tools in a WordPress developer’s toolkit. Whether you’re chasing down plugin conflicts, optimizing performance, or just learning how WordPress works under the hood, enabling debug mode gives you the visibility you need.
With proper setup—like using WP_DEBUG_LOG and hiding errors from public view—you can safely debug even on production environments without exposing vulnerabilities.
Now that you know how to enable and manage debug mode, you’re ready to take full control over diagnosing and fixing WordPress issues like a pro.
FAQs About Complete Guide to Enable Debug in WordPress
Q: Why You Should Enable Debug in WordPress?
A: Debugging is one of the most powerful tools in a WordPress developer’s toolkit. Whether you’re chasing down plugin conflicts, optimizing performance, or just learning how WordPress works under the hood, enabling debug mode gives you the visibility you need.
Q: How i can enable the debug in wordpress?
A: you can enable it using filezilla, cpanel or direct admin filemanager or using ssh if you are a pro.
Q: Enabling WordPress debug will fix my website errors?
A: no, it just a lead to find the problem and how it made easily, you can find conflicted plugin or file easier.
